Day :
- CardiovascularPharmacology|Ethnopharmacology|Immunopharmacology|Pharmacogenetics and PharmacogenomicsAdvances in Pharmacological Research
Location: Amphi Theater

Chair
Zhi-Yi Zhang
TESARO, Inc., USA

Co-Chair
Sanaa S Botros
Theodor Bilharz Research Institute, Egypt
Session Introduction
Layla Borham
Cairo University, Saudi Arabia
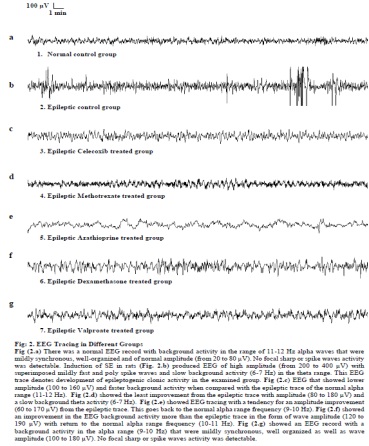
Title: The effect of some immunomodulatory and anti-infl ammatory drugs on Li-pilocarpine-induced epileptic disorders in wistar rats
Time : 12:30-13:00

Biography:
Layla Borham is a Professor of Clinical Pharmacology at Cairo University. She received her MSc and MD degrees at Cairo University Medical School. She has been working in Faculty of Medicine, Umm AlQura University, KSA for 15 years. During this period, she carried out a lot of scientific and social serving activities through her publications, scientific committee memberships, lectures and administrative work. She is a member in many committees in and outside the university. She is a Reviewer of Current Rheumatology Journal, and Associate Editor of Umm AlQura Medical Journal and Clinical Pharmacology and Translational Medicine Journal. She works in teaching hospitals as a Clinical Pharmacology Consultant. In addition, she works in the Ministry of Health hospitals and primary health care centres giving awareness lectures to health care providers and patients. She has been awarded a golden prize from Umm AlQura University for her overall services at the university.
Abstract:
Reham F Barghash
National Research Center, Egypt
Title: Current topics in computer-aided drug design technologies: Future aspects

Biography:
Abstract:
Mohammed Al Mohaini
King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Saudi Arabia
Title: Non-homologous end joining of complex DNA double-strand breaks with proximal thymine glycol and interplay with base excision repair
Time : 14:20-14:50

Biography:
Mohammed Al Mohaini is an Assistant Professor of Pharmacology at KSAU-HS, Saudi Arabia. His research interest is on “The effect of cancer chemotherapeutic drugs on the DNA especially the repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by these compounds”.
Abstract:
MarÃa Esperanza Avella Vargas
Military University of New Granada, Columbia
Title: Cardiovascular effects of Calea prunifolia H.B.K. in wistar rats

Biography:
María Esperanza Avella Vargas is a Professor of Pharmacology and Therapeutics in Medical and Surgical Clinic Area of the Faculty of Medicine at Military University of Nueva Granada. She is the leader of the research group-Pharmacology, Toxicology and Therapeutics-UMNG and responsible for the research seminar-study of preclinical and clinical research of medicines for its development and application. As PhD student, he belongs to the research group i.e., Search for bioactive principles in Colombian medicinal plants of the Department of Pharmacy of the Faculty of Sciences, National University of Colombia in the city of Bogotá.
Abstract:
Aim: Calea prunifolia HBK (Cp) has been traditionally used in Colombia as a medicinal plant known as carrasposa. It is attributed properties such as arterial hypotensive, antipruritic, antipyretic and anti-seborrheic. The aim of the study was to investigate the cardiovascular effect, based on the evaluation of blood pressure.
Materials & Methods: A specimen of Calea prunifolia HBK was identified and deposited in the Colombian National Herbarium of the Institute of Natural Sciences of the National University of Colombia. Leaf extract, aqueous extract (EACp), ethanolic extract (EECp), and fractions, such as the butanolic fraction (FBCp), were obtained. It was examined in isolated aorta and isolated vas deferens, as well as changes in blood pressure with chronic oral administration of the extracts and the fraction to normotensive Wistar rats and rats Wistar with hypertension induced by L-NAME. Th e evaluation was also performed with acute intraperitoneal administration of extracts and fraction to normotensive Wistar anesthetized rats and acute intravenous administration of the fraction. In addition, the activity of the angiotensin converting enzyme in plasma and cytosolic calcium was measured in cardiomyocytes and uterine cells.
Results: Chronic administration by oral route does not demonstrate a hypotensive effect between the different experimental groups. Acute intraperitoneal administration showed a significant decrease in blood pressure and heart rate of ECP. FBCp lowers blood pressure in anesthetized rats in a dose-dependent manner, evaluated at a range of 1-100 mg/kg, i.v. Cp did not aff ect the plasma activity of the angiotensin converting enzyme or cytosolic calcium in cardiomyocytes and uterine cells. But Cp relaxes the smooth muscle and changes the vascular tone favoring the decrease of the blood pressure in rats by mechanisms related to the alpha-adrenergic inhibition.
Conclusions: In this study, the hypotensive property traditionally attributed to Calea prunifolia HBK was not tested with the in vivo experimental models of chronic oral administration, considering that traditional use is through infusions of oral administration. There is difference with the positive effect on the isolated organ assays of aorta ring and vas deferens. These results, added to the effect demonstrated by the intravenous and intraperitoneal injectable parenteral administration, where the hypotensive effect is associated to a cardiopresor effect, which leaves other questions and opens a new way to continue in the study and knowledge of this plant.

Biography:
Vasiliki Daikopoulou has her expertise in Organic and Synthetic Chemistry. She has completed her Bachelor degree in Chemistry at Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and Master’s degree in Organic Synthesis and Natural Products at the same institute. She is currently working in R&D Department of R.G.C.C. S.A
Abstract:
A considerable number of substituted adenines have been reported to act as agonists or antagonists for several receptors and enzymes. They interact with adenosine receptors, which are found to be upregulated in various tumor cells. In order to enhance their medicinal properties, we decided to add a substituent with an equally significant biological activity. Quinazoline are organic compounds consisting of two fused six-membered aromatic rings, a benzene ring and a pyrimidine ring. Their own substituted derivatives are being synthesized constantly for medicinal purposes such as anticancer agents. Over the years, medicinal chemists have synthesized a variety of quinazoline derivatives by inserting various active groups to the quinazoline moiety using developing synthetic methods. Taking into consideration the above, we have created a pathway for the conjugation of these two molecules (adenine and quinazoline). The purpose of this study is to synthesize 9-(4-methoxyquinazolin-2-yl)-9H-purin-6-amine as a precursor of a final structure. Both 2-adenine-4-methoxy quinazoline and final compound are going to be studied for their possible biological and medicinal activity. The conjugation of adenine with 2-chloro-4-methoxy quinazoline is achieved by using a strong base and silica gel in high temperature via regioselective N-arylation via nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr).

Heba Abdel-Hady
Theodor Bilharz Research Institute, Egypt
Title: Characterization and evaluation of antioxidant activity of Ocimum canum leaves and its effeciency on Schistosoma mansoni larval stage

Biography:
Heba Abdel Hady is a Researcher of Medicinal Chemistry at Theodor Bilharz Research Institute (TBRI). She completed her BSc at Al-Azhar University; MSc and PhD in Biological Application of Natural Products. She carried out her research work on “Isolation and purification of the different classes of natural products which isolated from medicinal plants”. She has served as Editorial Board Member and Reviewer in some journals.
Abstract:
Schistosomiasis is the most endemic disease caused by trematode worm of the genus Schistosoma. Its control is dependent on kill the worm itself or one of its larval stages. The objective of this study is determination of the total phenolic and flavonoid contents, evaluating the scavenging inhibitory effect of Ocimum canum leaf methanol extract on DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) and ABTS as well as investigating the efficiency of plant extract against larval stages of Schistosoma mansoni. Also, chemical composition of plant extract was identified by GC-MS analysis. Antioxidant activity of the plant extract was evaluated by DPPH and ABTS scavenging assays while, cercaricidal and miracidicidal activity of it were tested at different concentrations directly on the larval stages for 2 hours, dead larvae were recorded each 30 minutes. The results revealed that Ocimum canum leaf methanol extract showed high total phenolic (321.78±0.69 mg GAE/g extract) and flavonoid contents (71.64±10.66 mg RE/g extract). Furthermore, there is a significant correlation between the concentration of the extract and the inhibition percentage of the free radicals. The higher inhibition percentage of plant extract was recorded by DPPH than ABTS at 500 µg/ml (84% and 62%) respectively; also, IC50 of DPPH and ABTS (26.41±1.39 and 194.45±2.03) respectively. Regarding to cercaricidal and miracidicidal activity, the plant extract showed larvicidal activity as it killed 82% of cercariae while, it was completely lethal to miracidia at 500 ppm within 2 hours. On the other hand, 36 chemical compounds were identified from plant extract. The main components are phytol (23%), hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester (15.48%), 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid methyl ester (14.99%), n-Hexadecanoic acid (7.62%), 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid (5.04%), ethyl linoleate (3.58%) and 2-propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-, methyl ester (3.17%). This study suggested that Ocimum canum can be used as cercaricidal and miracidicidal promising plant to control schistosomiasis disease as well as its potential use as antioxidant plant.

Biography:
Shaibu O Bello is the Dean of Faculty of Basic Medical Sciences, UDUS, Sokoto, Nigeria and has his expertise in pharmacology & Therapeutics. His passion is on population health as regards to adverse drug reaction and population pharmacokinetics especially in developing economies. He is also a trained Obstetrician where he again focuses on Obstetric pharmacology especially the effect of drugs on the feto-maternal duet. This is particularly important because, for ethical reasons, drugs are virtually not evaluated on fetus and mothers during development. He has contributed immensely to this field.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Drug choice and dose management are often tailored towards minimizing unwanted drug effects. Prescription writing also involves careful education of the patients on possible adverse effects, flags and what to do. In Africa, probably due to high level of health illiteracy, such information may be considered alarmist and undesirable by most patients. Meanwhile, most patient translates self-identifiable changes in the body as evidence of haven taken a ‘good’ drug. This study was designed to establish the extent of such unusual attitude to adverse drug effects in Northwestern Nigeria.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Questionnaire was designed using the modified Delphi protocol and validated. After ethical approval, multi-staged, cluster sampling technique was used to select local government regions, districts, and households for interviews. Only adults (>18yrs) who consented were interviewed. The domains of interest were demographics, expectations from drug treatments, knowledge, and attitudes towards common adverse effects of drugs.
Findings: Two hundred and thirty-five (235) persons were interviewed. Male female ratio was 7:3. Eighty three percent (83%) had no education beyond primary school level, while 53.4 percent has no western education at all. Seventy-eight percentage frequently combines orthodox and herbal medicine in any illness. Sixty percent would rather classify herbal agents as ‘strong’ rather than just ‘effective’. Forty three percent strongly believed that at least one of the following were evidence of potency of any orthodox drug: pain at injection site, dizzy spells, occasional vomiting, elation, stinging taste, bitter taste. Sixty seven percent of respondents were highly unlikely to complete more than 2 days’ dose of drugs that had no self-identifiable effect to suggest potency.
Conclusion & Significance: There appear to be high rate of health illiteracy in the studied population about adverse drug effects. This may have been due to translation from experiences with herbal agents. Such patients’ expectations should be factored into counselling.
Savita D Patil
H. R. Patel Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, India
Title: Anti-arthritic activity of marketed lauha bhasma

Biography:
Savita d Patil completed her M Pharm and PhD. Currently, she is a Vice Principal at H R Patel Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, India. She has worked in various areas like CVS, antihypertensive and hypolipidemic activity of indigenous plants, anti-asthmatic activity of both synthetic compounds as well as plant extracts, hepatoprotective activity using animal models, CNS related preclinical screening. She has guided more than 50 students for PG and five students are perusing PhD under her guidance.
Abstract:
Ayurveda is the system of medicine which first recognized the importance of metals and minerals for curing ailments. Lauha bhasma is a one of the mineral based ayurvedic medicine mentioned in ayurvedic classics indicated for sotha (inflammation) and sula (pain). Current study planned to provide scientific support to such folk claims. In current study marketed lauha bhasma was characterized using modern analytical techniques like SEM, EDAX and XRD. Pharmacological assessment of lauha bhasma at three different doses was carried out in Freund's Complete Adjuvant (FCA) induced arthritis administered at 0.1 ml dose in hind paw of rats which was evaluated by various parameters such as paw volume at 7,14, 21, 28 day, hematological (RBC, WBC, HB, ESR count), CRP and RF levels. On 28 day, rats were sacrificed & histopathology was done. We found that treatment with all three doses of lauha bhasma alters various hematological parameters, CRP and RF levels compared to control group. Even this alteration has also seen at histopathological studies. These alterations significantly found to be highest at increasing doses of selected bhasma. Thus, our results justifies folk claim about lauha bhasma as an anti-inflammatory drug.
- Neuropharmacology and Psychopharmacology | Clinical Pharmacology and Receptor theory | Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics | Toxicology | Biochemical Pharmacology
Location: Amphi Theater

Chair
Maria Esperanza Avella Vargas
Military University of New Granada, Columbia

Co-Chair
Vasiliki Daikopoulou
R.G.C.C. S.A., Greece
Session Introduction
Mihaly Balogh
Semmelweis University, Hungary
Title: 14-O-methylmorphine-6-O-sulfate, a novel opioid agonist displays peripheral antinociception following local or systemic administration

Biography:
Mihály Balogh is a PhD student and Assistant Research Associate at Semmelweis University (Budapest, Hungary) since 2015. He has experience in investigating different in vivo models of neuropathic (e.g. diabetic neuropathy) and inflammatory pain (e.g. CFA induced inflammation). He studies the role of the peripheral opioid system in analgesia and also acquired practice in several in vitro (e.g., western blot) and isolated organ assays. Beside his scientific work, he is involved in teaching pharmacology and pharmacotherapy at Semmelweis University for English and Hungarian students.
Abstract:
Background & Aim: Convincing data supports the contribution of peripheral opioid receptors to total antinociception produced by systemic opioids. To achieve that, the physicochemical property of test drug should be accounted. Herein, we examined the antinociceptive effect of 14-O-methylmorphine-6-O-sulfate (14-O-MeM6SU), in the rat formalin test after systemic or local administration.
Method: Pain events were induced by intraplantar 2.5% formalin solution. Then, pain events were counted for 60 min, subdivided into 5 min periods. The 0-10 and 11-60 min time periods were named as phase I and phase II, respectively. Drugs were injected subcutaneously (s.c.) or intraplantarly (i.pl.), 15 or 5 min prior to i.pl. formalin injection, respectively. The impact of test compounds on both phases was studied. Additionally, righting reflex method was used to exclude the central effect of test compounds as its impact on sleeping time induced by inhaled isoflurane. Vehicle injections were used as control. One way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test and unpaired t-test was used for the determination of significances in case of formalin test and righting reflex method, respectively.
Results: S.c. injections of 14-O-MeM6SU or morphine inhibited the pain events evoked by formalin in both phases. Co-administered naloxone methiodide (NAL-M), a peripherally acting opioid antagonist reversed the antinociceptive effect of certain s.c. 14-O-MeM6SU doses but not of morphine (Fig. 1.). Morphine injected into ipsilateral or contralateral paws showed antinociception in both pain phases. Interestingly, 14-O-MeM6SU in certain doses produced antinociception only after ipsilateral injections. Finally, 14-O-MeM6SU contrary to morphine in s.c. antinociceptive doses significantly prolonged the sleeping time of inhaled isoflurane. These results indicate that the novel morphine analogue reported to have high efficacy earlier by us, have limited access to CNS and may have peripheral antinociception that is of potential clinical value.

Sarah Hassan
University of Strasbourg, France
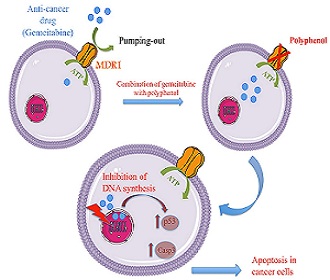
Title: Polyphenols potentialize the cytotoxic activity of gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer cell line AsPC-1

Biography:
Sarah Hassan is a PhD student at University of Strasbourg. She holds Master’s degree in Pharmacology from Holy Spirit University of Kaslik and BS in Biochemistry from Lebanese University. Her research and thesis focused in anticancer drugs, enhancing their efficacy and reducing their toxicity potential by their combination with natural substances.
Abstract:
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers, with only about 5% of patients surviving 5 years past the initial diagnosis. Gemcitabine monotherapy is the standard of treatment for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer since several decades. Despite advances with current chemotherapy combinations, overall survival outcomes are still require novel therapeutic approaches. Here, we examined the efficacy of combined treatments of polyphenols and gemcitabine in human pancreatic cancer cells. For that purpose, the proapoptotic effects of gemcitabine were studied on the human pancreatic cell line AsPC-1 in presence or absence of several polyphenols, in order to evaluate if they latter are able to potentialize gemcitabine cytotoxicity. Our study aims to investigate the implication of MDR1 (multidrug transporter) in resistance to gemcitabine and if the studied polyphenol could target this drug efflux pump in AsPC-1 cells by flow cytometric analysis. We observed that 5 µM/ml gemcitabine in combination with 50 µM of selected polyphenol (catechin, quercetin, bergamottin, rhamnetin) was more effective than gemcitabine alone, as shown by increased in the percentage of dead cells up to 60%. In addition, our results indicate that the combination of gemcitabine and each polyphenol increased the expression levels of cleaved caspase-3 and the regulator of apoptosis p53. Moreover our results demonstrated that some polyphenols inhibit the efflux activity of MDR1. Our study in vitro suggests therefore that chemotherapy with gemcitabine might be significantly increased upon combination with specific polyphenol. In conclusion, polyphenols may be promising agents for novel combination therapy since they potentialize the cytotoxic activity of gemcitabine to eradicate pancreatic cancer and therefore the cellular resistance.
Yuzhu Zhang
Longhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of TCM, China
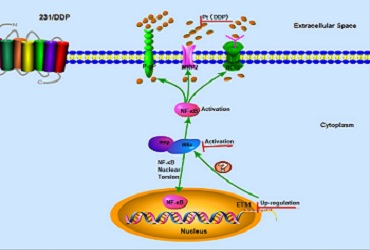
Title: ETS1 is associated with cisplatinum resistance though IKKα/NF-βB pathway in MDAMB-231

Biography:
He is studying his PhD of medicine at Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
His researches focus on key target genes of tumor prognosis, mechanisms of drug resistance and anti-cancer natural drugs.
Abstract:
MDA-MB-231/DDP had higher IC50 value of DDP, lower intracellular DDP concentration, lower apoptosis ratio than MDA-MB-231 cell line treated with DDP. Considering the intracellular DDP concentration difference, we tested drug-resistant membrane proteins (MRP2, P-gp and BCRP), which were remarkably increased in MDA-MB-231/DDP cells. Next, we found these increased membrane proteins were induced by the activation of NF-κB pathway in MDA-MB-231/DDP cells. Furthermore, ETS1, RPL6, RBBP8, BIRC2, PIK3A and RARS were six important genes for DDP-resistance based on PPI network and expression validation. However, it has been reported enforced over-expression of ETS1 induced IKKα mRNA and protein expression as well as IKKα promoter activity. Our results suggested the protein expression of ETS1 and IKKα were significantly up-regulated in MDA-MB-231/DDP cells. In addition, inhibition of ETS1 expression enhances chemo-sensitivity to DDP and reversed the activation of NF-κB pathway in MDA-MB-231/DDP cells, whether ETS-1 binds to the core IKKα promoter and strongly induces its activity. Now, our team is researching the corresponding sites between ETS1 and IKKαby dual-luciferase and chromatin immunoprecipitation technique (ChIP).
Yueqi Li
East China University of Science and Technology, China
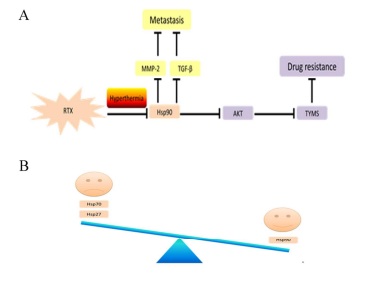
Title: Hyperthermia adds to chemotherapy suppress peritoneal metastasis from colorectal cancer and enhance the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of raltitrexed by downregulating Hsp90

Biography:
Yueqi Li is pursuing her PhD since 2013 at East China University of Science and Technology. Her research work mainly focuses on “The administration of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy”. She tries to explore the biochemical targets for the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from colorectal cancer.
Abstract:
The poor prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) with peritoneal metastasis has not been improved up to now. Over the last few years, the therapy of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) following macroscopic surgery has been safely used in clinic. The aim of this study is to clarify the mechanism of peritoneal carcinomatosis suppression and the enhancement of chemotherapeutic sensitivity by the administration of HIPEC. Specifically, we build a peritoneal metastatic xenograft model to analyze the effect of HIPEC. Peritoneal injection was performed that CRC cells in phosphate-buffered saline solution were injected into the intraperitoneum of mice. Interestingly, we find the metastasis is efficiently inhibited and the number of metastatic nodules is remarkably reduced by HIPEC therapy compared with conventional chemotherapy. The Hsp90 is down-regulated by treating with hyperthermia after raltitrexed (RTX). In particular, the metastasis inhibition is indicated by the suppressing of TGF-β and MMP-2 and the chemo-sensitivity enhancement is shown by the attenuating of Akt activation and the expression of thymidylate synthase (TYMS). The overexpression of Hsp90 reverses the enhanced effects of the addition of hyperthermia. And the pharmacologic inhibition of Hsp90 enhances the effects. Together, our study provides a preclinical proof for better evaluation of combined hyperthermia and chemotherapy for peritoneal metastatic carcinoma treatment.
Masoumeh Gholami
Tarbiat Modares University, Iran
Title: Assessing the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and voltage dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) in synaptic plasticity induced by the combined application of tetanic stimulation and pentylenetetrazol in hippocampus area CA1 of sodium salicylate treated rats

Biography:
Masoumeh Gholami is a PhD student in Human Physiology at Tarbiat Modares University, Iran.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Pentylenetetrazol (PTZ), a GABAA receptor antagonist, is one of the most extensively used epileptogenic agents. PTZ-induced seizures cause a number of seemingly permanent biological alterations in the hippocampus and other brain regions. These alterations may play an important role in synaptic plasticity. In vitro, a brief PTZ application (3 mM, 10 min) did not potentiate the slope of field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) but induced along lasting enhancement of the amplitude of population spikes (PSs). Given the widespread use of salicylates (main metabolite and active component of aspirin) in clinical practice and to explore the relationship between tolerance to salicylate, long-term potentiation (LTP), and hippocampal activity, we studied whether tolerance to sodium salicylate would augment the plastic effect of a brief exposure to PTZ, and whether quantized priming via a natural stimulus pattern prior to PTZ exposure would change the lasting effects of PTZ.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: To assess whether priming would alter PTZ-induced plastic changes in the CA1 region, primed burst stimulation (PBs) sequences were applied on hippocampal slices taken from chronic sodium salicylate (NaSal) treated rats prior to the PTZ protocol (3 mM, 10 min). The underlying molecular mechanisms (NMDARs vs. VDCCs) of the long-term potentiation (LTP) induced by the 4PBs plus PTZ combined treatment in the NaSal group were also studied.
Findings: We noted priming with a natural pattern of stimulus trains prior to PTZ (4PBs-PTZ) can uncover the effects of chronic salicylate at the synaptic level that NMDA receptors activity and the VDCCs may involve in the phenomenon.
Conclusion & Significance: The elucidation of changes in synaptic plasticity following chronic salicylate could be useful in the clinical practice when aspirin is chronically prescribed in the medication program of some diseases such as cardiovascular diseases.
Sleman Kadan
Al-Qasemi Academic College, Israel
Title: Gundelia tournefortii anti-diabetic efficacy: Chemical composition and GLUT4 translocation

Biography:
Sleman Kedan is a PhD student at Al-Qasemi Research Center, Al-Qasemi Academic College, and Casali Institute for Applied Chemistry, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel where he completed his MSc in Chemistry in 2010. His PhD thesis entitled “Novel anti-diabetic natural drug candidates: isolation, identification and characterization of the chemical structures and biomolecular mechanisms”. He has published four refereed papers.
Abstract:
In the present in vitro study, we tested the chemical composition, cytotoxicity and anti-diabetic activity of two wild artichoke-like vegetable, Gundelia tournefortii, and distinct extracts: methanol and hexane. GC/MS phytochemical analysis of Gundelia tournefortii methanol and hexane extracts revealed 44 compounds reported here for the first time in Gundelia tournefortii. Out of the 50 detected compounds only stigmasterol was present in both extracts. The efficacy of Gundelia tournefortii extracts in enhancing glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4) translocation (fig. 1) to the plasma membrane (PM) was tested in L6 muscle cells stably expressing myc-tagged GLUT4 (L6-GLUT4myc) using cell-ELISA test. Results obtained here indicate that methanol and hexane extracts were safe up to 250 µg/ml as measured with MTT and the LDH leakage assays. The methanol extract was the most efficient in GLUT4 translocation enhancement. It increased GLUT4 translocation at 63 µg/ml by 1.5 and 2 folds relative to the control in the absence and presence of insulin, respectively. These findings indicate that Gundelia tournefortii possesses anti-diabetic activity in part by enhancing GLUT4 translocation to the PM in skeletal muscle.

Biography:
Fadhila Helnisa has completed her Bachelor degree from Andalas University, Indonesia and has successfully fulfilled all the academic requirements of Indonesian Pharmacist Profession. Now, she is studying Master of Toxicology at University of Birmingham.
Abstract:
A study on clinical pharmacokinetics aspect of drugs in patients with hypertension at the Internal Medicine department of Hospital Padangpanjang (Indonesia) has been conducted. The aims of the research were to determine the accuracy of antihypertensive medications to achieve targeted blood pressure and to assess the dosage regimen based on liver and/or kidney functions, also drug interactions. The study was performed from December 2013 to February 2014. This is observational prospective study with 49 patients who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data was analyzed descriptively. Results showed that 60.42% antihypertensive medications were effective but 39.58% not effective to reach the targeted blood pressure. There were three cases in appropriate dose regimen covering one case digoxin, one case furosemide and one case captopril. From the cases, doses exceed individual dose included digoxin and captopril. There were 14 cases of pharmacokinetic interactions and two cases of pharmacodynamics interactions. Interaction between amlodipine and diltiazem (7 patients, 14.58%) influenced the blood pressure control in patient. These are pharmacokinetic interaction because diltiazem decreases metabolism of amlodipine by inhibiting enzyme CYP 3A3/4.
Tie Teck Kim
Changi General Hospital, Singapore
Title: Consider Ertapenem as culprit for central nervous system related adverse effects
Biography:
Tie Teck Kim has completed his BPharm from Curtin University of Technology in Western Australia in 2007 and his Master’s degree in Infectious Diseases from the University of Western Australia in 2014. He is currently practicing as an Antimicrobial Stewardship Pharmacist at Changi General Hospital.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Ertapenem use has been associated with central nervous system (CNS) related adverse effects (AEs) which include delirium, hallucinations, altered mental status (AMS), stroke like symptoms and seizures. We describe baseline characteristics and clinical features in four patients who developed CNS related AEs while receiving ertapenem during a period of six consecutive months in 2016.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: We retrospectively reviewed patients on ertapenem and identified the ones who developed CNS related AEs attributed to ertapenem use from April till October 2016.
Findings: Patient one (no renal impairment) was prescribed ertapenem for complicated intra- abdominal infection. He was noted to be drowsy on day 12 of ertapenem. Over the next 1-2 days, he developed auditory hallucinations, jerky limb movements and fluctuating level of consciousness. He was switched to aztreonam. Patient two (no renal impairment) developed confusion and hallucinations (visual, auditory and tactile) on day 25 of ertapenem which was being administered for tubo-ovarian abscess. Ertapenem was substituted to meropenem. Patient three (known end stage renal failure) developed seizure while on day 28 of ertapenem which was prescribed for bilateral renal abscess. No further episode of seizure was observed after ertapenem was switched to piperacillin/tazobactam. Patient four (known chronic kidney disease) was receiving ertapenem for complicated urinary tract infection. He was noted to be delirious on day nine of ertapenem. Patient was switched to meropenem. In these patients, average age was 65 years. Male to female ratio was 1:1. None of the patients had previous history of seizure or CNS disorders. Two patients had normal renal functions. Toxic & metabolic causes were excluded. Computed tomography (CT) of brain was normal in all cases. Dose was renally adjusted in two patients. Ertapenem therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) was not locally available. Symptom improvement was noted 3-4 days after ertapenem discontinuation in all patients.
Conclusion & Significance: Patients who develop these AEs can deteriorate rather unexpectedly which leads to extensive investigations and increase in health care cost. The cost can be minimized if physicians are acquainted to consider ertapenem as an offender agent. However appropriate workup to eliminate alternate etiology also needs to be considered at the same time as dictated by the clinical scenario. Ertapenem TDM might give information on CNS AEs in future studies.











